The journal/conference papers I have published are shown below.
(2021) Intimate Partner Violence and Its Relationship with Psychological Distress Among Older Asian Americans: Results from the California Health Interview Survey
Chien-Ching Li, Alicia K. Matthews, Pei-Shan Yen, Yi-Fan Chen, and XinQi Dong, “Intimate partner violence and Its Relationship with Psychological Distress Among Older Asian Americans: Results from the California Health Interview Survey”, Asian Journal of Psychiatry. Vol 63, 102798, 2021.
Objective
This study aimed to examine the influence of intimate partner violence on psychological distress among a diverse sample of older Asian Americans living in California. Methods: Participants in the 2007–2009 California Health and Interview Survey (CHIS) aged fifty years and older and self-reported as Asian Americans were included in the study. The primary independent variable was the history of any intimate partner violence (physical or sexual violence) since 18 years of age. The Kessler Psychological Distress Six-item Scale was used to measure the study dependent variable. A composite score (0–24) was created for psychological distress during the past 30 days as well as for the one month in the past 12 months when they were at their worst emotionally. Other covariates, including acculturation and demographic factors, were measured. Hierarchical multivariate linear regressions were conducted to examine the influence of intimate partner violence on psychological distress after adjusting for covariates. Results: In the study, about 8% of older Asian Americans reported ever experiencing intimate partner violence. After controlling for the level of acculturation and demographic factors, a history of intimate partner violence was significantly associated with higher levels of psychological distress for the past month (beta =2.07, SE =0.74, p <0.05) and for the worst month in the past year (beta =1.99, SE =0.68, p <0.05).
Conclusion:
Intimate partner violence is a significant risk factor for distress among older Asian Americans. Culturally targeted violence prevention efforts and treatment approaches for individuals impacted by violence are needed in this highly underserved segment of older Americans.
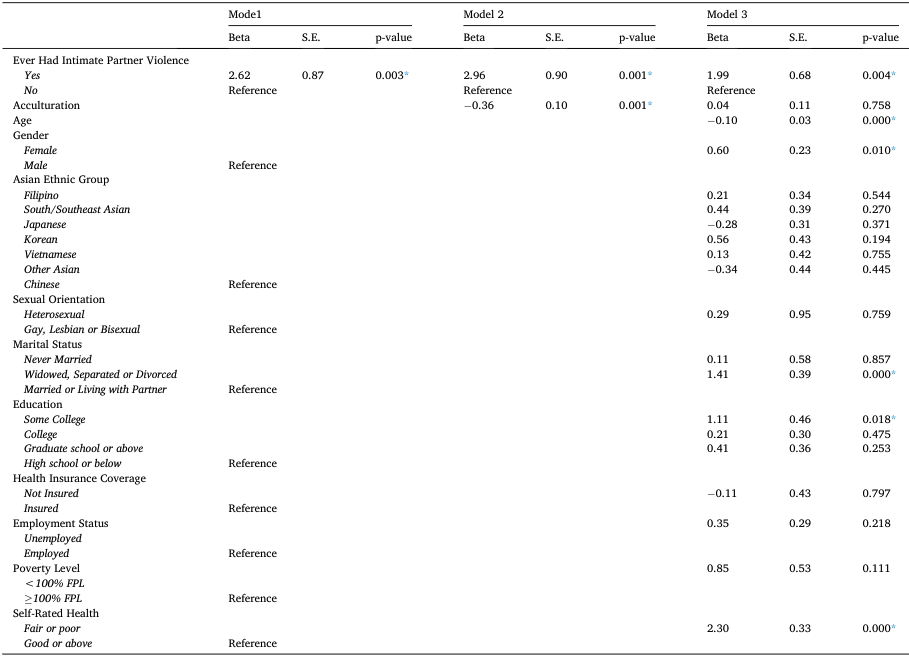
(2021) The influence of perceived discrimination in healthcare settings on psychological distress among a diverse sample of older Asian Americans
Chien-Ching Li, Alicia K. Matthews, Pei-Shan Yen, Yi-Fan Chen and XinQi Dong, “The influence of perceived discrimination in healthcare settings on psychological distress among a diverse sample of older Asian Americans”, Aging & Mental Health. DOI: 10.1080/13607863.2021.1958146, 2021.
Abstract
This study utilized a retrospective cross-sectional study design. The dataset was obtained from 2015-2017 California Health Interview Survey (CHIS). Healthcare discrimination experience (yes, no) was measured using the following question “Over your entire lifetime, how often have you been treated unfairly when getting medical care (never, rarely, sometimes, often)?”. Psychological distress was the study outcome and was measured using the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale. A composite score (0-24) was created for psychological distress for the prior 30 days and for the worse most in the past 12 months. A hierarchical multivariate linear regression was conducted to examine the influence of healthcare discrimination experience on psychological distress after adjusting for other covariates…’
Method
This study utilized a retrospective cross-sectional study design. The dataset was obtained from 2015-2017 California Health Interview Survey (CHIS). Healthcare discrimination experience (yes, no) was measured using the following question “Over your entire lifetime, how often have you been treated unfairly when getting medical care (never, rarely, sometimes, often)?”. Psychological distress was the study outcome and was measured using the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale. A composite score (0-24) was created for psychological distress for the prior 30 days and for the worse most in the past 12 months. A hierarchical multivariate linear regression was conducted to examine the influence of healthcare discrimination experience on psychological distress after adjusting for other covariates.
Results
Study participants (weighted N = 1,360,487) had a mean age of 64.35 years (SD = 0.61), were primarily female (54.93%), heterosexual (96.61%), and married or living with a partner (73.37%). About 10.00% of older Asian Americans ever perceived healthcare discrimination over their entire lifetime. Perceived discrimination was associated with higher levels of psychological distress for the past 30 days (beta= 2.107, SE = 0.662, p < 0.05) and for the worst month in the past year (beta= 2.099, SE = 0.697, p < 0.05) after controlling for covariates.
(2016) Big data: The data wisdom and knowledge-based economics
Jack C.S. Yue and Pei-Shan Yen, “Big data: The data wisdom and knowledge-based economics”, Tsang Hai Publishing, Taiwan. 2016.
This book serves to address the principle ideas of big data from a statistical point of view. It begins with illustrating how to correctly define a problem, which is the core of big data analysis. Next, the book details the relation between big data and statistical sampling methods. Following this is the explanations of how to exercise various sampling techniques to collect big data. Then how to analyze big data systematically is addressed in detail. The last two chapters of this book provide some actual big data examples encountered by the authors.

(2014) The design and optical analysis of compound parabolic collector
Chia-Wei Kuo, Pei-Shan Yen, Wen-Chey Chang, and Keh-Chin Chan, “The design and optical analysis of compound parabolic collector”, Procedia Engineering. Vol. 79, pg. 258-262, 2014.’
For various applications of solar thermal energy, the compound parabolic collector (CPC) is frequently used. To overcome the major limits of a traditional CPC, including a rapid increase in height for a larger aperture width and a low concentration ratio, a modified design was proposed in this paper. This research follows the recent study of Jadhav et al., which used only the region below the common focus of parabolas. Through optical analysis, a design modification was achieved by adjusting the vertical position of the receiver. From the results, setting the height of the receiver to 0.46 times the aperture width was found to permit a greater collection range of incident rays. In addition, a better method for evaluating the performance of the CPC was proposed using an intercept factor to account for the total reflection phenomenon caused by the receiver. By applying the approach to different cases of focal length, it was shown that the concentration ratio was not strongly affected by an increasing focal length owing to the low correlation between the concentration ratio and focal length.
(2010) An international study of 2010 population census methods
Pei-Shan Yen and Jack C.S. Yue, “An international study of 2010 population census methods”, Journal of Population Studies. Vol 40, pg. 203-229, 2010
The objective of the population and housing census is to collect the demographic information of a nation or an area which is used for government planning and policy making. However, the traditional census in recent years is facing new challenges, such as the increase in survey cost, non-response rate, and data demand. Although most countries still use the traditional census method for 2010 census, many are seeking new methods to improve the quality of census data and to reduce the survey cost. The 2010 Taiwan Census will no longer use the traditional method and use registered-based census with sampling survey instead. It will integrate the official registry system to acquire the basic demographic characteristics, and collect more detailed information on the social and economic topics, including personal information about education, fertility, and elder care by using sampling methods. The new method is adapting the experiences from Singapore, Netherland, and the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden). However, the new method should be evaluated carefully since Taiwan is well-known for having some unique population characteristics. Thus, we will evaluate the new census methods from other countries and see if they are suitable to use in Taiwan. We shall first introduce and compare the traditional and new methods in conducting population census.. The new methods include Registered-Based Census, Registered-Based Census with Sampling Survey, and the Rolling Census. For the second half of paper, we will further examine the survey methods that will be used for the U.S. and French census, including the design concept and the sampling method executed by the American Community Survey (ACS) to replace the long-form questionnaire for the 2010 U.S. Census. In addition, we will discuss the restrictions of using sampling survey to collect data, and compare the traditional census to new census methods. Finally, we will use examples to demonstrate the problems of using registered-based population to estimate the De Jure (or permanent resident) population in 2010 Taiwan Census.
